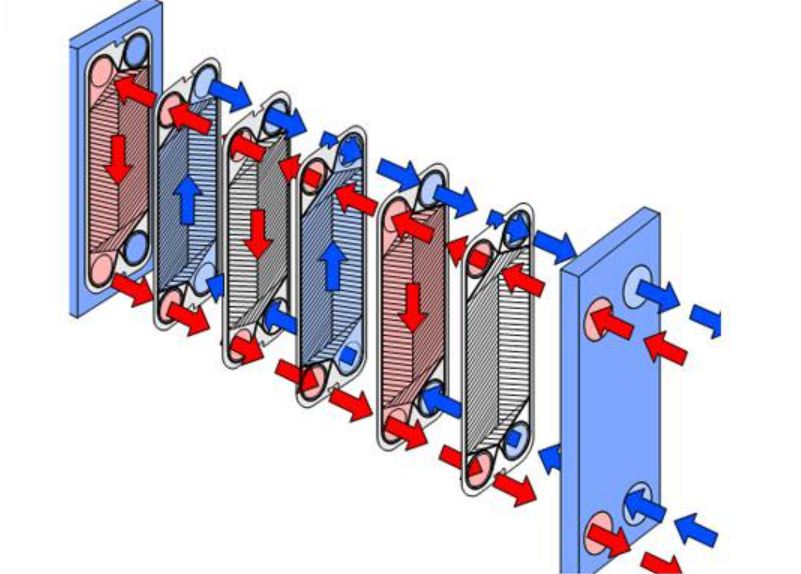
What is a Heat Exchanger?
Heat pumps are useful for cutting down on energy use and improving energy efficiency in an eco-friendly manner. The growing satisfaction worldwide with HVAC technology is driving the search for better ways to make heat exchangers more efficient.
The heat exchanger is crucial for keeping the whole heat pump system running smoothly. While all heat pump exchangers follow similar basic designs, top-notch heat pumps need the best possible heat exchangers. Let's delve into how heat exchangers work, their design, suitability, and other important aspects.
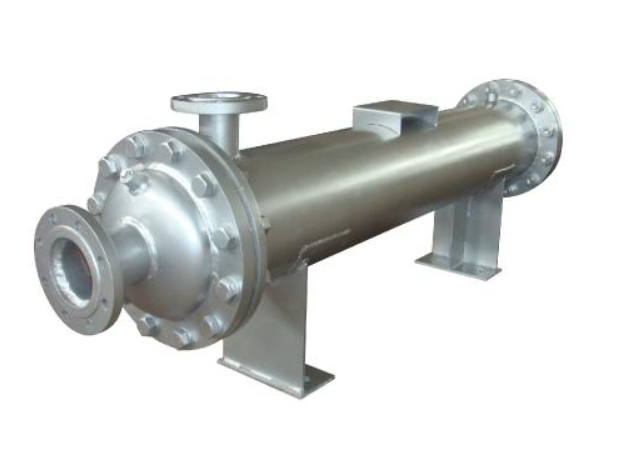
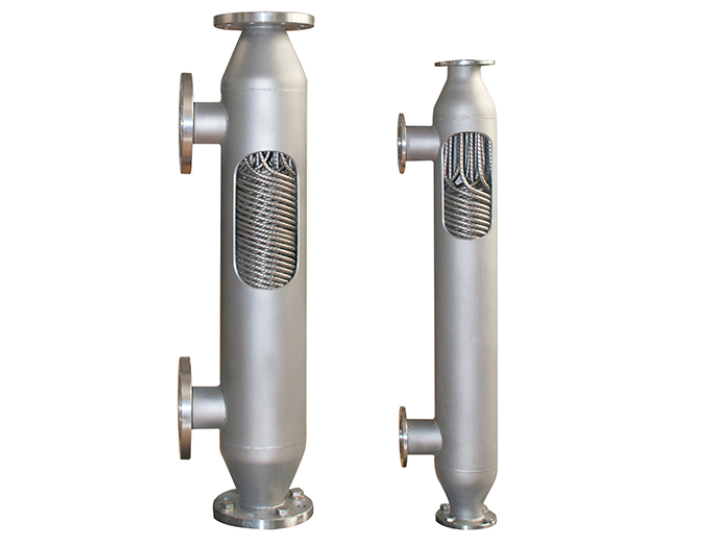



What Is a Heat Exchanger?
A heat exchanger is a device that deals with the essential aspects of the heat energy process. It operates based on the principles of thermodynamics, enabling heat transfer between fluids with different properties. There's a spectrum of heat exchanger designs, spanning from conventional to modern innovations.
The specific design features are influenced by various applications such as industrial processing plants. Heat exchangers have gained widespread acceptance in HVAC systems due to their efficient temperature regulation and cost-effectiveness. Their utilization in refrigeration systems is also widely embraced.
How Is Heat Exchanged?
Thermal dynamics principles govern how heat is transferred within the device. Heat naturally moves from areas of high temperature to those of lower temperature. Heat pump systems primarily transfer heat from a heat source to a heat sink, operating on the principle of moving heat rather than generating it.
Various modes of heat transfer ensure that the process occurs efficiently within the coolant. A heat exchanger isn't a single unit but rather a combination of coils, plates, tubes, and other components working together to facilitate heat exchange. Let's delve deeper:
● Conduction - This involves the transfer of heat between molecules with different kinetic energies. When molecules collide, those with higher energy transfer heat to those with lower energy. Heat exchangers utilize walls that act as barriers between fluids, facilitating conduction. They operate based on Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction, continuing until thermal equilibrium is reached.
● Convection - Governed by Newton's Law of Cooling, this process involves the transfer of thermal energy as molecules move along the heat exchanger's walls. Heated molecules expand and rise due to their lower density, transferring heat to cooler molecules as they move. This continual process creates a convection current.
● Thermal Radiation - In this process, electromagnetic energy is emitted from a high-temperature surface. Unlike conduction and convection, radiation doesn't require a transfer medium and flows freely.
Types of Heat Exchanger
Different kinds of heat exchangers serve various functions, with the indirect contact type being one category. These heat exchangers employ plates and tubes as partitions, ensuring that the fluids involved do not mix during the heat exchange process.
Typically constructed from metal, the walls of the tubes or plates are key components. Indirect heat exchangers can be further classified into:
● Plate Heat Exchangers - These devices consist of thin plates closely packed together, allowing for separate fluid flow. They typically employ a countercurrent flow configuration and offer customization options such as pillow fins or plate fins.
● Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers - This type comprises multiple tubes housed within a larger cylindrical enclosure. The tubes are isolated, with fluids flowing inside and on the outer surface of the heat exchanger tubes. Shell and tube heat exchangers support both countercurrent and concurrent flow configurations and are compatible with both single and double-phase fluids.
How Does Heat Exchanger Work?
How Heat Exchangers Operate
Heat exchangers are instruments designed to enable the transfer of heat between fluid molecules of differing temperatures. Air conditioner heat exchangers are compatible with a diverse array of fluid types categorized as process fluid or utility fluid.
Refrigerant is a commonly employed fluid in modern heat pumps, which are vital components in various industries for both heating and cooling operations.
Functioning of Heat Exchangers in HVAC Systems
Primarily, HVAC systems utilize space for the exchange of thermal energy. The heat exchanger within HVAC systems functions by exchanging heat and cold air. Issues with heat exchangers can significantly impact the overall performance of the HVAC system.
A malfunctioning heat exchanger fails to facilitate the heat exchange process, leading to discomfort and compromised air quality within the building.